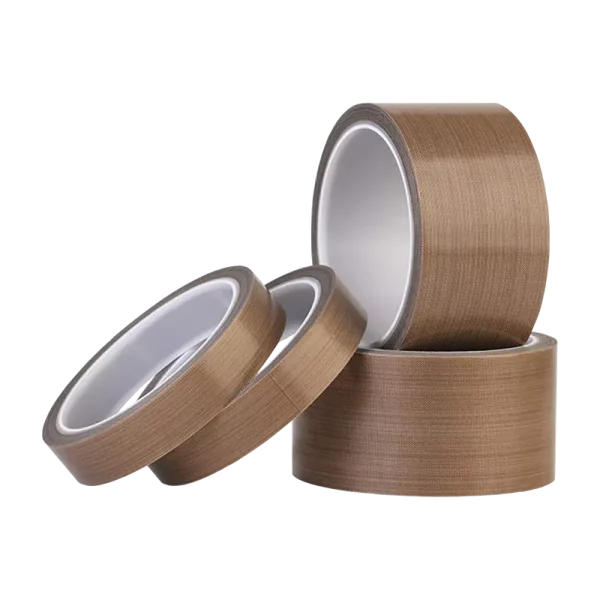
Introduction
In the modern industrial landscape, high-performance materials play a crucial role in ensuring the efficiency, safety, and longevity of equipment and systems. One such material that has stood the test of time for its exceptional thermal, chemical, and mechanical properties is Teflon. Specifically, high-temperature Teflon products, including tapes, sheets, fabrics, and coatings, are indispensable in industries such as aerospace, automotive, electronics, and food processing.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of high-temperature Teflon — covering its composition, physical and chemical properties, manufacturing processes, types, key applications, benefits, limitations, and maintenance guidelines.
What is Teflon?

Teflon is the trade name for polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), a synthetic fluoropolymer of tetrafluoroethylene (TFE). It was first discovered by Roy Plunkett in 1938 while working at DuPont. PTFE is well known for its low coefficient of friction, high-temperature resistance, chemical inertness, and non-stick properties.
High-temperature Teflon refers to specialized PTFE products engineered to maintain their integrity and performance under elevated temperature conditions, typically in the range of -190°C to +260°C (and occasionally up to 300°C for short periods).
At the end of the article, there are selected product recommendations. Welcome to check them out.
Chemical Composition of High-Temperature Teflon
At a molecular level, PTFE is composed of a carbon backbone chain surrounded by fluorine atoms. The molecular formula is (C₂F₄)ₙ, where n represents the number of repeating units. This unique chemical structure provides PTFE with its exceptional properties:
- Carbon-carbon bonds form a strong and stable backbone.
- Fluorine atoms create a protective shield around the carbon chain, making it chemically inert and resistant to environmental degradation.
Some high-temperature Teflon products may be modified with fillers such as glass fiber, carbon, bronze, or graphite to improve mechanical strength, dimensional stability, or wear resistance.
Key Properties of High-Temperature Teflon

- Exceptional Thermal Resistance
- Continuous operating temperature range: -190°C to +260°C
- Peak resistance up to 300°C for limited periods
- No melting point in conventional sense — it transitions gradually
- Chemical Inertness
- Resistant to virtually all chemicals, including acids, alkalis, and solvents
- Unaffected by UV radiation and weathering
- Low Coefficient of Friction
- One of the lowest among solid materials (~0.05 to 0.10)
- Provides excellent anti-stick and non-stick surfaces
- Electrical Insulation
- Outstanding dielectric strength
- Low dissipation factor and high surface resistivity
- Non-Toxic and Food Safe
- FDA-approved grades available for food processing and medical use
- Hydrophobic and Oleophobic
- Repels water and oil-based substances, reducing contamination
- Mechanical Stability
- Retains flexibility and tensile strength under varying temperatures
Manufacturing and Forms of High-Temperature Teflon Products
High-temperature Teflon is available in various forms tailored for specific applications:
- Teflon Tapes: Skived or coated PTFE film with adhesive backing, used for sealing, insulation, or non-stick surfaces.
- Teflon Coatings: Spray-applied PTFE coatings on cookware, industrial equipment, or machinery.
- Teflon Sheets: Solid or expanded PTFE sheets for gaskets, linings, and covers.
- Teflon Rods and Tubes: Machined for bearings, seals, and insulators.
- Teflon Fabrics: Woven fiberglass impregnated with PTFE for conveyor belts, heat-sealing machines, and architectural membranes.
Manufacturing Process:
- Polymerization: Tetrafluoroethylene monomers polymerized under high pressure.
- Paste Extrusion: For thin films and tapes.
- Ram Extrusion: For rods and tubes.
- Skiving: Large PTFE billets shaved into thin sheets or tapes.
- Coating: PTFE emulsions sprayed and sintered onto substrates.
- Impregnation: Fiberglass fabrics impregnated with PTFE dispersions and cured.
Key Applications of High-Temperature Teflon

Aerospace
- Wire and cable insulation for aircraft
- Heat shields and gaskets
- Fuel hose liners
Automotive
- Heat-resistant gaskets and seals
- Non-stick surfaces in engine parts
- Hose and tubing for fuel systems
Food Processing
- Non-stick conveyor belts
- PTFE-coated baking sheets and molds
- Sealing bands on packaging equipment
Electronics
- Insulation for high-voltage components
- Printed circuit board coatings
- Semiconductor manufacturing equipment
Textile and Garment
- Heat-sealing and pressing belts
- Protective barriers and liners
Chemical Industry
- Lining for tanks and pipelines
- Chemical-resistant gaskets and seals
- Diaphragms in pumps and valves
Medical
- Catheters and surgical instruments
- Coatings for implants and prosthetics
- Non-stick surfaces for pharmaceutical processing
Advantages of High-Temperature Teflon
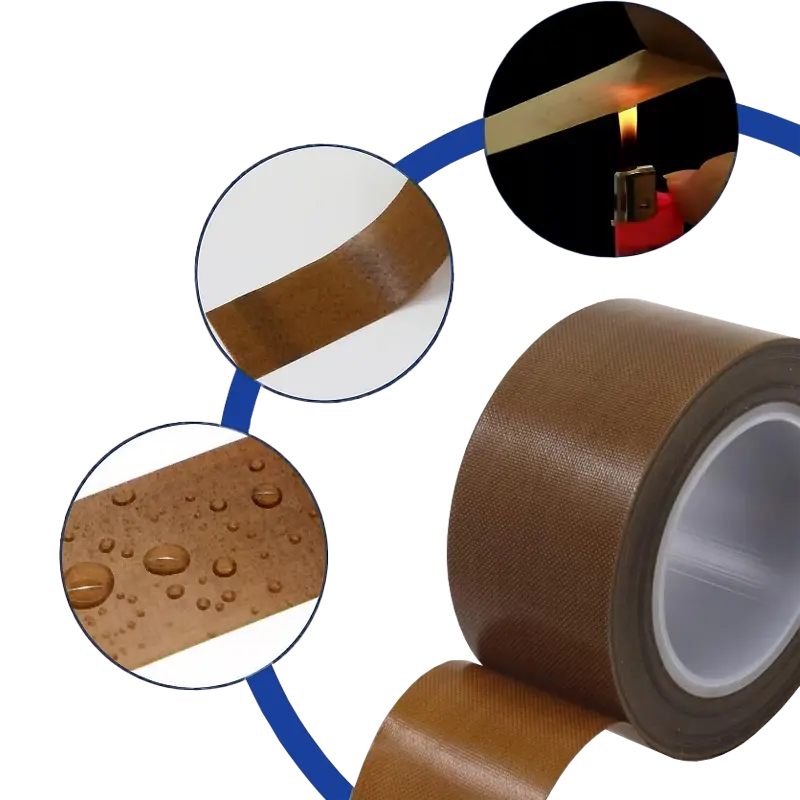
- Wide temperature tolerance
- Excellent chemical resistance
- Low friction, anti-stick surface
- Superior electrical insulation
- Weather and UV resistant
- Non-toxic, food-safe options available
- Easy to clean and maintain
- Compatible with other materials like glass, metal, and composites
Limitations of High-Temperature Teflon
While high-temperature Teflon is an outstanding material, it has a few limitations:
- High Cost: More expensive than conventional plastics.
- Low Wear Resistance: Pure PTFE is soft and prone to deformation under high loads.
- Difficult Bonding: Non-stick surface makes adhesive bonding challenging.
- Creep Behavior: Tends to deform under prolonged stress at elevated temperatures.
- Limited Mechanical Strength: Can be improved with fillers but remains lower than metals and engineering plastics.
How to Use and Maintain High-Temperature Teflon Products
Installation Tips:
- Ensure clean and dry surfaces when applying Teflon tape or coatings.
- Use compatible adhesives or mechanical fasteners for mounting sheets or fabrics.
- Avoid sharp edges or high-impact forces during installation.
Maintenance Guidelines:
- Clean surfaces with mild detergents or solvents; avoid abrasive tools.
- Inspect regularly for wear or degradation, especially in moving parts.
- Replace or recoat when the surface loses its non-stick or insulating properties.
Storage Recommendations:
- Store in a cool, dry, and dust-free environment.
- Protect from prolonged exposure to direct sunlight.
- Avoid stacking heavy objects over flexible products like tapes and fabrics.
Future Trends and Innovations
With advancements in material science, PTFE and its high-temperature variants are continuously evolving:
- Nano-reinforced PTFE composites for enhanced wear resistance and strength.
- Multi-layered PTFE laminates for improved barrier properties.
- High-purity PTFE materials for ultra-clean environments in semiconductor and medical industries.
- Recyclable and eco-friendly PTFE variants to address environmental concerns.
Conclusion
High-temperature Teflon stands as a material of choice where extreme temperatures, aggressive chemicals, and stringent hygiene standards are present. Its unique combination of thermal, chemical, electrical, and mechanical properties makes it invaluable across a wide array of industrial sectors.
From aerospace to food processing, its applications are extensive, offering reliable performance under the harshest conditions. Understanding its composition, characteristics, benefits, limitations, and maintenance requirements helps industries optimize its use and unlock its full potential.
As innovation continues, the future of high-temperature Teflon looks even brighter, with enhanced performance capabilities and broader application possibilities on the horizon.
High Temperature Teflon Tape
1.Teflon Tape.
2.Material: PTFE Coated Fiberglass
3.Glue:silicone
4.Heat resistant:-70 to 260℃
5.Thickness mm: 0.08-0.25
6.Colour Available:BLACK/BROWN
7.Usage: specialy designed to perform as heat sealing and converting industrial.

Products
Rich variety of adhesive tape

